“Domain” is a term you come across often when researching the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). But what are CMMC domains, exactly? In today’s post, we tell you everything you need to know about this crucial component of the CMMC ecosystem.
A Definition of CMMC Domains
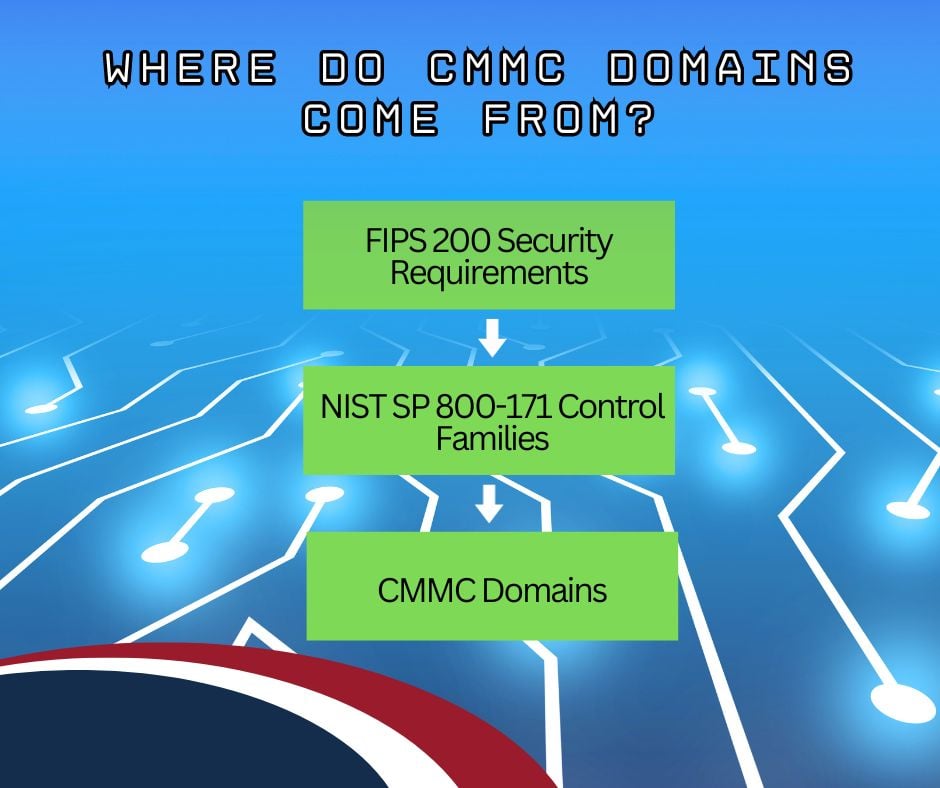
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) domains are groups or categories of cybersecurity practices. CMMC domains are based on the control families outlined in NIST SP 800-171, “Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Nonfederal Systems and Organizations.”
In turn, the NIST SP 800-171 families are closely aligned with the 17 minimum-security requirements described in Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 200, “Minimum Security Requirements for Federal Information and Information Systems.”
While NIST SP 800-171 uses the term “control families,” the CMMC equivalent terminology is “domain.” However, both NIST SP 800-171 control families and CMMC domains share the same purpose and names.
How Many CMMC Domains Are There?
Just as with NIST SP 800-171 control families, there are 14 CMMC domains. Each CMMC domain refers to a broad area of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) protection. The number of practices within each CMMC domain may vary.
CMMC domains are associated with a two-letter abbreviation. Below is the full list of the fourteen CMMC domains with their respective abbreviations:
- Access Control (AC)
- Awareness & Training (AT)
- Audit & Accountability (AU)
- Configuration Management (CM)
- Identification & Authentication (IA)
- Incident Response (IR)
- Maintenance (MA)
- Media Protection (MP)
- Personnel Security (PS)
- Physical Protection (PE)
- Risk Assessment (RA)
- Security Assessment (CA)
- System and Communications Protection (SC)
- System and Information Integrity (SI)
CMMC Domains: Descriptions
In this section, we will go through the 14 CMMC domains to understand what they cover and why they are important to your cybersecurity posture.
- Access Control (AC): Limits information system access to authorized users, processes acting on behalf of authorized users, or devices.
- Awareness & Training (AT): Aims to ensure that organizational personnel are adequately trained to carry out their assigned information security-related duties and responsibilities.
- Audit & Accountability (AU): This group of practices is geared toward creating, protecting, and retaining information system audit records and ensuring that the actions of individual information system users can be uniquely traced to those users.
- Configuration Management (CM): Practices within this domain establish and maintain baseline configurations and inventories of organizational information systems.
- Identification & Authentication (IA): This domain focuses on ensuring that organizations can identify users, processes acting on behalf of users, or devices and authenticate (or verify) the identities of those users, processes, or devices.
- Incident Response (IR): These practices track, document, and report incidents to appropriate organizational officials and/or authorities.
- Maintenance (MA): Domain centered around performing periodic and timely maintenance on organizational information systems.
- Media Protection (MP): Practices within this domain protect information system media, both paper and digital; limit access to information; and sanitize or destroy media containing CUI before disposal or release for reuse.
- Personnel Security (PS): Ensures that information systems containing CUI are protected during and after personnel actions such as terminations and transfers.
- Physical Protection (PE): These practices limit physical access to information systems, equipment, and the respective operating environments to authorized individuals.
- Risk Assessment (RA): Identifies risks to organizational operations, organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, and the Nation, resulting from the operation of a system.
- Security Assessment (CA): Deals with the testing or evaluation of security controls to determine the extent to which the controls are implemented correctly.
- System and Communications Protection (SC): This group of practices ensures that an organization is actively identifying, managing, and controlling all system and communication channels that store or handle CUI.
- System and Information Integrity (SI): These practices ensure that technology assets containing CUI are continuously monitored to detect malicious activity.
Need To Achieve CMMC Compliance? We Are Here To Help
Whether it’s CMMC, NIST SP 800-171, DFARS, or ITAR, we help organizations achieve compliance with all applicable cybersecurity regulations at any level so that they can win and maintain Department of Defense (DoD) contracts.
Brea Networks, LLC is a fully Registered Provider Organization (RPO) and is a Microsoft partner with full Microsoft GCC High licensing and migration solutions.
Contact our CMMC Registered Practitioners today by clicking here.
Brea Networks, LLC / CMMCCompliance.us
451 W. Lambert Rd Suite 214
Brea, CA 92821
Tel: (714) 592-0063